Significance Of CSF Test In The Diagnosis Of Neurological Conditions
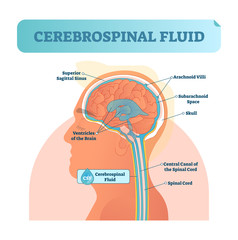
Cerebrospinal Fluid(CSF) is a transparent liquid that surrounds and protects the brain and spinal cord. An intricate network of cells called Choroid plexus secretes Cerebrospinal fluid.
A CSF test is an invasive test performed in a diagnostic center that helps diagnose medical conditions that affect the central nervous system, that mainly consists of the brain and spinal cord. Your doctor may order for a CSF test when he/she suspects that the symptoms that you’re experiencing are due to a medical condition involving your brain and spinal cord.
A CSF test is a series of tests that checks:
- Cerebrospinal Fluid protein
- Cerebrospinal Fluid cell count
- Cerebrospinal Fluid differential cell count
- Cerebrospinal Fluid colour, clarity and pressure
- Cerebrospinal Fluid glucose
Why Is It Done?
CSF test helps in diagnosing a variety of medical conditions and diseases that affect the brain and spinal cord, such as:
- Infections like encephalitis(inflammation within the brain), meningitis(inflammation of the membranes that cover the central nervous system) and fungal infections. With the diagnostic tests, your doctor can determine whether microorganisms like bacteria, viruses, fungi or parasites are causing the infection or not.
- Haemorrhaging or bleeding around the brain
- Autoimmune diseases like Multiple sclerosis( a chronic progressive illness that affects the central nervous system), Guillain-barre syndrome( a condition in which the immune system attacks the peripheral nerves), sarcoidosis(A disease in which clumps of inflammatory cells develop in multiple organs) and neurosyphilis(an infection of the brain and spinal cord).
- Metastatic cancer(cancer that spreads to other body parts from its site of origin) or tumours
- Alzheimer disease, a progressive, neurological disorder.
When Is It Ordered?
When you are experiencing a combination of symptoms along with fever and flu-like symptoms. They are:
- Change in consciousness and mental status
- Depression and mood swings
- Nausea
- Fatigue
- Headache, which is sudden, intense and incessant in nature
- Tremor or numbness
- Lack of coordination and difficulty while walking and speaking
- Dizziness
- Sensitivity to light
- Muscle weakness
- Seizures, confusion or hallucination
The Test Procedure
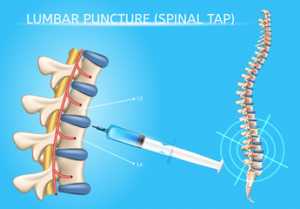
The most commonly used method for obtaining Cerebrospinal fluid is Lumbar puncture or spinal tap. The patient will have to either lie down in a fetal position or a normal sitting position. As an initial step, the healthcare provider will clean the puncture site using an antiseptic, and an anaesthetic is injected into the lower spine. The healthcare provider will insert a spinal needle into your spinal canal, and the opening pressure reading is taken. 1 to 10 mL CSF fluid will be collected in multiple vials(mostly four vials).
Before withdrawing the spinal needle, the closing pressure reading is also obtained. After removing the needle, the puncture site is cleaned, a bandage and some pressure are applied over the needle site. You will be asked to lie down, without lifting your head for an hour or more after the test. The test lasts for less than half an hour.
What Do the Results Indicate?
If the CSF test results come back normal, then it means that there is nothing abnormal found within the cerebrospinal fluid. All the components of CSF that were measured in the test are within the normal range. Normal values of CSF components are:
- Chloride: 110 to 125 mEq/L
- Cerebrospinal Fluid glucose: 50 to 80mg/100mL
- CSF total protein: 15 to 60mg/100mL
- Cerebrospinal Fluid cell count: 0 to 5 WBC(white blood cells)
- Gamma globulin: 3 to 12% of the total protein
- Pressure: 70 to 180mm H2O
- The appearance of CSF: Colourless and clear
If the sample appears cloudy, then it may indicate infection or accumulation of protein or WBC. A red or bloody sample may indicate spinal cord obstruction or bleeding. Whereas, yellow, orange or brown, sample may indicate the presence of a higher amount of CSF protein.
CSF Glucose
The high glucose level in CSF can be a sign of more elevated blood sugar. The low glucose level in CSF can be due to a variety of conditions like
- Hypoglycemia( lower than average level of blood sugar)
- Meningitis(inflammation of the membranes that cover the central nervous system) or other types of meningitis
- Tuberculosis

CSF Protein
The increased protein level in the CSF can be due to
- Inflammatory or infectious conditions,
- Blood in the CSF
- Tumour
- Diabetes
- Polyneuritis( a condition where peripheral nerves are damaged)
The decreased protein level in the CSF can be a sign of rapid production of cerebrospinal fluid.
Blood Cells in CSF
High white blood cell count may indicate:
- Demyelinating disease, such as multiple sclerosis
- Meningitis
- An abscess (buildup of pus inside the tissue)
- Acute infection
- Tumour
- Beginning of a chronic condition
If RBCs are present in your sample, then it can be as a result of traumatic lumbar pressure or bleeding into the spinal cord.
Gamma Globulin in CSF
High level of gamma globulin in CSF can be a sign of
- Multiple sclerosis
- Guillain barre syndrome
- Neurosyphilis
CSF Pressure
Elevated CSF pressure may arise as a result of increased intracranial pressure.
Lower CSF pressure may arise as a result of:
- Leakage of cerebrospinal fluid
- Spinal block(spinal anaesthesia)
- Fainting
- Dehydration
Frequently Asked Questions
Why do I need a lumbar puncture? Why can’t my blood or urine be tested?
The spinal fluid is the apt sample that can be used to diagnose conditions that affect your central nervous system since the fluid surrounds and protects both your brain and spinal cord. But certain serious conditions or diseases that affect the central nervous system may change the various elements of CSF, which can easily be detected by CSF testing. CSF test, in conjunction with the blood or urine test, can help evaluate your current medical condition.
What are the other methods used to collect CSF samples?
Besides lumbar puncture, ventricular puncture or cisternal puncture are also used for collecting CSF samples. During a ventricular puncture, an opening is made in the skull, and a needle is inserted into any of the brain’s ventricles. During a Cisternal puncture, a needle is inserted into the occipital bone(the bone that covers the base of the skull) to obtain a CSF sample.
What are the preparations required before the test?
Before undergoing a CSF test, you will be asked to empty your bowels and bladder. You need to fast for 3 hours before the test. It’s important to inform the healthcare provider about the blood-thinning medicines or aspirin that you are taking. For instance, clopidogrel, warfarin and over the counter pain relievers like naproxen sodium, ibuprofen, or aspirin. Inform your healthcare provider if you’re allergic to local anaesthetics.
What is the normal volume of CSF?
The total volume of CSF in adults ranges from 90 to 150mL, whereas 10 to 60 mL in infants. The liquid is continuously secreted, circulated, and absorbed back into the blood. Even though about 500mL of CSF is produced per day, it will be later on replaced every few hours.
Is there any reason I shouldn’t get a CSF Test?
CSF test is dangerous if you have low platelet count in blood, blood clotting disorder, or tumour at the back of your brain. This is also applicable if you’re taking clopidogrel, blood thinners or aspirin or other drugs to reduce blood clot formation.