COVID Antibody Test: Purpose, Procedure and Result Interpretation
COVID-19 antibody test or serology test measures protective proteins called antibodies in your blood. During a viral infection, our immune system produces antibodies, or immunoglobulins, as a response to foreign substances called antigens. Covid Antibody tests are often done to check whether a person had COVID-19 in the recent past and have developed antibodies against SARS-CoV-2(Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2) infection. The test is also used to confirm whether the person has recovered from SARS-CoV-2 or not.
Who Should Take a COVID Antibody Test?
You can probably get tested for antibodies if:
- You’re tested positive for COVID-19 yet completely recovered
- You assume that you might have come into contact with SARS-CoV-2, but didn’t experience any new symptoms for the past 10 days. The symptoms are difficulty in breathing, loss of taste or smell, dizziness, feeling weak, seizures, diarrhoea, and slurred speech.
- You’re not experiencing symptoms associated with COVID-19.
- You didn’t have a fever for the past 24 hours.

The COVID antibody test may not be right for you if you are:
- Diagnosed with the virus less than ten days ago
- Was exposed to SARS-CoV-2 directly in the past 14 days
- Currently having a disease that weakens your immune system
- Had a fever during the past 24 hours or feeling sick
- Want to know whether you’re infected with SARS-CoV-2
When Can This Test be Done?
The type of covid antibody test and the time of taking the test have an impact on the accuracy of this test. The test won’t detect antibodies if you’re getting tested too early only when the antibodies are developing in your blood. So most likely your healthcare professional won’t recommend this test at least 14 days after the symptoms start.
Another factor that reduces the accuracy of this test significantly is Cross-reactivity. This means there is a chance of cross-reaction between the antibody assays specifically designed for SARS-CoV-2 and related viruses such as SARS-CoV, common coronavirus). This gives false-positive test results.
What Happens During a Covid Antibody Test?
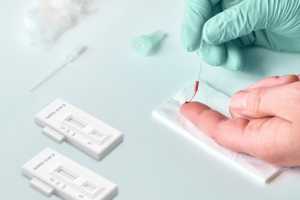
Based on the availability of tests, the eligibility may differ. A healthcare professional will take your blood sample, typically through a finger prick, or by inserting a needle into a vein in your arm. Your blood sample is tested to detect one or more types of antibodies to the virus, such as:
IgM antibodies- These antibodies occur early in an infection.
IgG antibodies- These antibodies appear later
IgM is the first antibody in the blood upon infection, whereas IgG is the type of antibody found in abundance in our blood.
Antibodies are produced at the end of 7 days or one week after getting infected. After 14 days, IgM reaches its peak. Whereas, IgG antibodies form in a person’s body 14 days after the onset of symptoms. After 8 to 13 days, IgG typically becomes positive and IgG reaches its peak around 21 days.
The major method of this test involves analysing the binding of specific antibodies to targeted antigens, or viral proteins. The most commonly used platforms to conduct COVID antibody tests are:
- Lateral Flow assay
- Chemiluminescent immunoassay
- Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay(ELISA)
Within an assay, both the targeted antigens and the blood samples are incubated. If the antibody produced against the virus is found in your blood, then it will bind to the antigen, and thus a positive covid antibody test results will be obtained.
What Do the COVID Antibody Test Results Indicate?
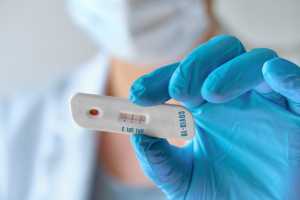
- If you’re tested positive for COVID-19 antibodies, then it may indicate that you were infected with the virus in the past. This also might mean that you have some immunity to SARS-CoV-2.
- If your COVID antibody test results are false positive, then it means you have antibodies in your blood and had a different kind of SARS-CoV-2.
- Whereas, if you test negative, then you didn’t come into contact with the virus, or you didn’t have the virus for a long time, to produce antibodies.
- It’s possible to test negative, yet have SARS-CoV-2 and not have antibodies. This is a False-negative result.
No matter the test results, you don’t need a follow-up, if you don’t have any symptoms. But in case if you have, then you may need to take a diagnostic test to check for signs of active virus.
Since there are chances of getting false-negative results, after getting tested, it’s essential that you follow safety guidelines. Stay home as much as possible, often wash your hands and wear a mask when you’re out.
COVID Antibody Test For Asymptomatic Person
A person who isn’t experiencing the symptoms of SARS-CoV-2 is an asymptomatic person. The symptoms include fever, cough and body ache. Even if you’re an asymptomatic person, you can take the COVID antibody test, since your body might be fighting off the virus, showing no result. You can confirm the exposure with the virus, by taking a COVID antibody test.
Frequently Asked Questions

If I have symptoms that I think might be that of COVID-19, then do I need a COVID antibody test?
No. The test is not used to diagnose SARS-CoV-2. If you’re experiencing any COVID-19 symptoms, such as fever, cough, muscle pain, shortness of breath, diarrhoea, etc, then you have to talk to your doctor about taking a diagnostic test, such as an RT-PCR that detects the virus.
Should I get the antibody test or the RT-PCR test, if I don’t have any symptoms?
It’s recommended to take an antibody test if you’re previously tested positive for the virus or don’t have any symptoms even if you had close contact with someone tested positive for the virus. It is also applicable if you had a previous history of COVID-19 like symptoms. But it’s also recommended waiting for two weeks, after the symptoms appear, in order to take an antibody test.
Do I need to follow social distancing even if I have antibodies?
Yes. It’s extremely important that you maintain social distance as well as follow safety guidelines because by having antibodies, it’s not certain that you’re immune to SARS-CoV-2 infection in future. Added to that, even if a person is not infected, he/she can transmit viral particles right from their face, hands and other body parts. This will only increase the chances of infection to the rest.
Can children take COVID antibody test? Is there a reduced accuracy for this test in the case of children?
There is no minimum age limit for taking an antibody test. However, no research has indicated the reduced accuracy for this test in children. The antibody test involves a simple blood draw and sometimes can be challenging for young children since they should remain still during the blood draw and the needle insertion causes mild pain.
What are the Prerequisites For Taking COVID Antibody Test?
There are no specific requirements for an antibody test. The test can be taken with or without Doctor’s prescription as such. There are neither any specific diet recommendations nor a need for 12 hours of mandatory fasting.
Am I eligible to donate my plasma, if I have COVID-19 antibodies?
You may be able to help COVID-19 affected patients if you have completely recovered from the disease, through donating your plasma. Your plasma now contains the antibodies since your body has fought SARS-CoV-2. Therefore, your plasma can help fight off the disease that patients face.